There are a lot of ways in securing the information that is being transmitted. One of the ways is Cryptography. Some of the information has already been provided in Block chain and Cryptography. As of now, we shall discuss cryptography types and in the consecutive writings its algorithms, tools, and applications. We shall now dive in.

Cryptography is the method of transmitting secured data and communications via few codes so that only the destined person knows about the actual information that is transmitted. This form of process intercepts unauthorized accessibility for the data. So, in clear the name itself indicates that “crypt” refers to “hidden” to “writing”.
Remember Alice and Bob? When Alice sends a message to Bob, the message can be interpreted by Mallory directly. Now, if we use cryptography here, Mallory will not be able to access message directly. We will look into several types of it.
Symmetric Key Cryptography:

It is an encryption system where the sender and receiver of message use a single common key to encrypt and decrypt messages. This is also termed as Private or Secret key cryptography. Symmetric Key Systems are faster and simpler but the problem is that sender and receiver have to somehow exchange key in a secure manner. Again there are several classifications in symmetric key cryptography.
Note: Ciphertext or Cyphertext is the result of encryption performed on plain text using an algorithm, called a cipher.
Stream Cipher: It is a method of encrypting text (to produce ciphertext) in which a cryptographic key and algorithm are applied to each binary digit in a data stream, one bit at a time. This method is not much used in modern cryptography. The main alternative method is the block cipher in which a key and algorithm are applied to blocks of data rather than individual bits in a stream.
Block cipher: A block cipher is an encryption method that applies a deterministic algorithm along with a symmetric key to encrypt a block of text, rather than encrypting one bit at a time as in stream ciphers. A block cipher takes a block of plain text bits and generates a block of ciphertext bits, generally of same size. The size of block is fixed in the given scheme. The choice of block size does not directly affect to the strength of encryption scheme. The strength of cipher depends up on the key length. Following are the classifications in block cipher encryption:
- Data encryption standard (DES) has been found vulnerable against very powerful attacks and therefore, the popularity of DES has been found slightly on decline. DES is a block cipher, and encrypts data in blocks of size of 64 bit each, means 64 bits of plain text goes as the input to DES, which produces 64 bits of cipher text. The same algorithm and key are used for encryption and decryption, with minor differences. The key length is 56 bits.
- Triple DES: The speed of exhaustive key searches against DES after 1990 began to cause discomfort amongst users of DES. However, users did not want to replace DES as it takes an enormous amount of time and money to change encryption algorithms that are widely adopted and embedded in large security architectures. The approach was not to abandon the DES completely, but to change the manner in which DES is used. This led to the modified schemes of Triple DES (sometimes known as 3DES).
The encryption-decryption process is as follows:
- Encrypt the plain text blocks using single DES with key K1.
- Now decrypt the output of step 1 using single DES with key K2.
- Finally, encrypt the output of step 2 using single DES with key K3.
- The output of step 3 is the ciphertext.
- Decryption of a ciphertext is a reverse process. User first decrypt using K3, then encrypt with K2, and finally decrypt with K1.
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): It is the more popular and widely adopted symmetric encryption algorithm likely to be encountered nowadays. It is found at least six time faster than triple DES. A replacement for DES was needed as its key size was too small. With increasing computing power, it was considered vulnerable against exhaustive key search attack. Triple DES was designed to overcome this drawback but it was found slow.
The features of AES are as follows −
- Symmetric key symmetric block cipher
- 128-bit data, 128/192/256-bit keys
- Stronger and faster than Triple-DES
- Provide full specification and design details
- Software implementable in C and Java
- IDEA (International Data Encryption Algorithm): It is an encryption algorithm. It is a symmetric block cipher which takes 64 bit as a input, 28-bit key and performs 8 identical rounds for encryption in which 6 different sub keys are used and four keys are used for output transformation.
- Twofish: It is an encryption algorithm designed by Bruce Schneier. It’s a symmetric key block cipher with a block size of 128 bits, with keys up to 256 bits. It is related to AES and an earlier block cipher called Blowfish. Twofish was actually a finalist to become the industry standard for encryption, but was ultimately beaten out by the current AES.
Asymmetric key Cryptography:
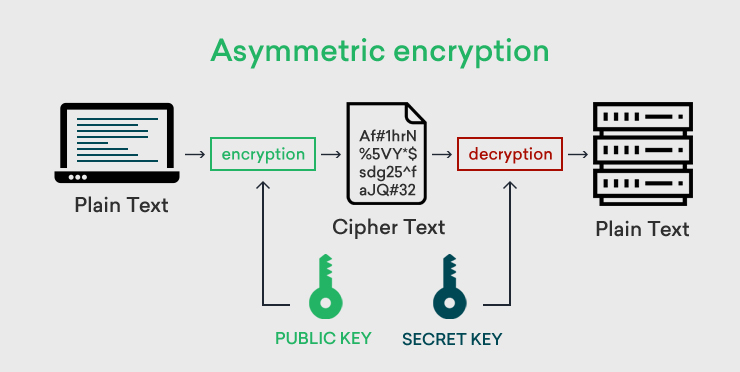
This is also termed as Public-key cryptography. It follows a varied and protected method in the transmission of information. Using a couple of keys, both the sender and receiver go with encryption and decryption processes. A private key is stored with each person and the public key is shared across the network so that a message can be transmitted through public keys. The more details go here!
Hashing

Hashing is a method of cryptography that converts any form of data into a unique string of text. Any piece of data can be hashed, no matter its size or type. In traditional hashing, regardless of the data’s size, type, or length, the hash that any data produces is always the same length. A hash is designed to act as a one-way function — you can put data into a hashing algorithm and get a unique string, but if you come upon a new hash, you cannot decipher the input data it represents. A unique piece of data will always produce the same hash. More learning!
As we have already discussed, the concepts are vast and we are trying our best for a better writing. Please go through the references for more information that we are unable to place it here.
Citations:
- What is Cryptography?
- Cryptography Techniques
We shall have more postings on the Asymmetric and Hashing techniques of Cryptography is possible soon. Till then, you can refer to the provided links. Have a happy and Safe learning.
Stay Home Stay Safe!
3 thoughts on “Cryptography and its types”