Hello peeps! After a detailed study I bring to you a summarized python blog that you will need to know before you get started.
This is the module one , will have more coming up later….I have tried my best to cover variables, lists, functions, methods and packages with some useful examples. It is a short read with useful content hence , do give it a read to brush up with a quick revision if you are already familiar.
Variables
Variables have associated values assigned to a name or reference.
Data Types of variables :
- int for integers
- float for real numbers
- Boolean for true and false
- string for text
2 important functions related to variables :
- To convert one data type to other: float(variable name)
Ex. Print(“hey”+ str(5) + “years from now”)
- To get type of variable
Type(variable) or print(type(var))
EXAMPLE: A,B and C are variables of different type
- A=5
- B=”hey”
- C=5.56
LISTS
- It is a compound data type.
- Collection of objects under a single name.
- Can have different data type objects including sublists.
- List type has specific functionality and behaviour.
Sub-setting or accessing a list:
Indexing basically starts from 0
To access ,
- The third element in the list list[2]
- The last element in the list list [-1]
Slicing a list : getting a range of values from the list
Syntax:
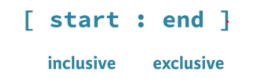
Example:
- List[3:] 4th element to the last
- List[:4] from beginning till the fourth element
- List[-4:] last four elements
Manipulating lists: Add, change or remove elements from a list.
- Adding : done by “+” symbol
Ex: List + [“hey”] –adds element to existing list
- Deleting element: done by del function ,it immediately updates the indexing values as per the new list.
Del(list[3]) -deletes 4th element of the list
- Changing or updating list with assignment operator i.e =
List[3]=5 , will change the 4th element to 5
NOTE:
The variables are actually reference to the same data element . For example, X is a list, Y is another list with values of X If Y is updated, then values in X will change too.
To avoid such scenarios,
Copy list as :
Y = list(X) or using slice method: Y =X[:]
Fun Fact : “;” in python is used to place commands in same line,

Functions
Function is a Piece of reusable code, it is used to solve a particular task
Some example of standard built-in functions:
- Type(var)
- Max()- gives maximum element in a list ,passed as parameter
- Round()- can have one or two parameters:
Syntax:
Round (number, precision)
Round (number)— round it off to nearest integer
- Len(var) -gives length
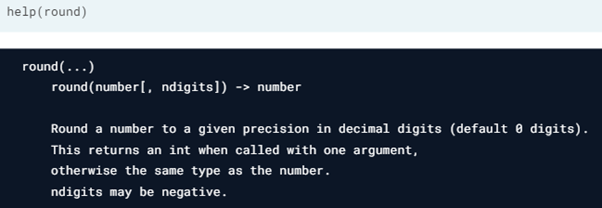
- Help(function name) will tell you the functionalities of the function, or how to use a particular in built function.
Fun Fact : square brackets in help function indicate that the parameter may or may not be added.
Sorting in python:
Remember those days when we had to do the tedious job of writing 5-6 lines of code for sorting, well python provides that as an in-built function, via sorted
sorted() takes three arguments: iterable, key and reverse
By default key is none and reverse is false.
Ex: sorted(list,key=None,reverse=True) will return a descending ordered list
METHODS:
Methods are functions that belong to an object , every object depending on its type has associated methods
List methods : count() , index()
- List.count(4) – returns number of times 4 occurs in the list
- List.index() -returns the index of the list
Some other list methods:
- append(), that adds an element to the list it is called on,
- remove(), that removes the first element of a list that matches the input, and
- reverse(), that reverses the order of the elements in the list it is called on
String methods:
string.capitalise()- puts your string’s first letter in caps
string.replace(‘s’,’ze’) -will replace s in your string with ze
string.upper()- will capitalise the entire string
Packages
Having all the functions in a large code database can be difficult to maintain and can be very messy to extract.
Hence python introduces a unique feature i.e packages
Packages is directory of python scripts (or modules). It has specific function,modules and type
Packages that we have seen earlier are :
- Numpy for arrays
- Matplotlib for data visualisation
- scikit learn for machine learning Installing and importing packages
Here’s a very easy way to installing and importing your packages:

Importing your package:
- IMPORTING WITH ALIAS:
- import numpy as np
- np.array([1,2,3])
- SELECTIVE IMPORTING:
- import numpy as array
- array([1,2,3])

That’s all for today folks, most of y’all might know the basics that i have covered in this blog , but I believe that that basics build up the ideals of the subject. Hence, I started with the very first fundamentals of ML with python. Enjoy and have a great day! Please like if you found this useful in any way:)