Prim’s algorithm is used to find the minimum spanning tree from a graph. It finds the subset of edges that includes every vertex such that the total of the weights of edges should be minimum. How this is done? Will go through the step-by-step procedure!
Algorithm:

Step 1: From the given graph, remove all loops and parallel edges. The one with the maximum weight of the parallel edges should be removed. According to Fig 1.1, remove the loop around F and the parallel edge of BD that has maximum weight 8. That gives the below i.e. Fig 1.2

Step 2: Choose any arbitrary node as root from the graph. To be more precise, according to Greedy Algorithm, the vertex that has minimum weight has to be chosen. So, let us choose E from Fig 1.2.
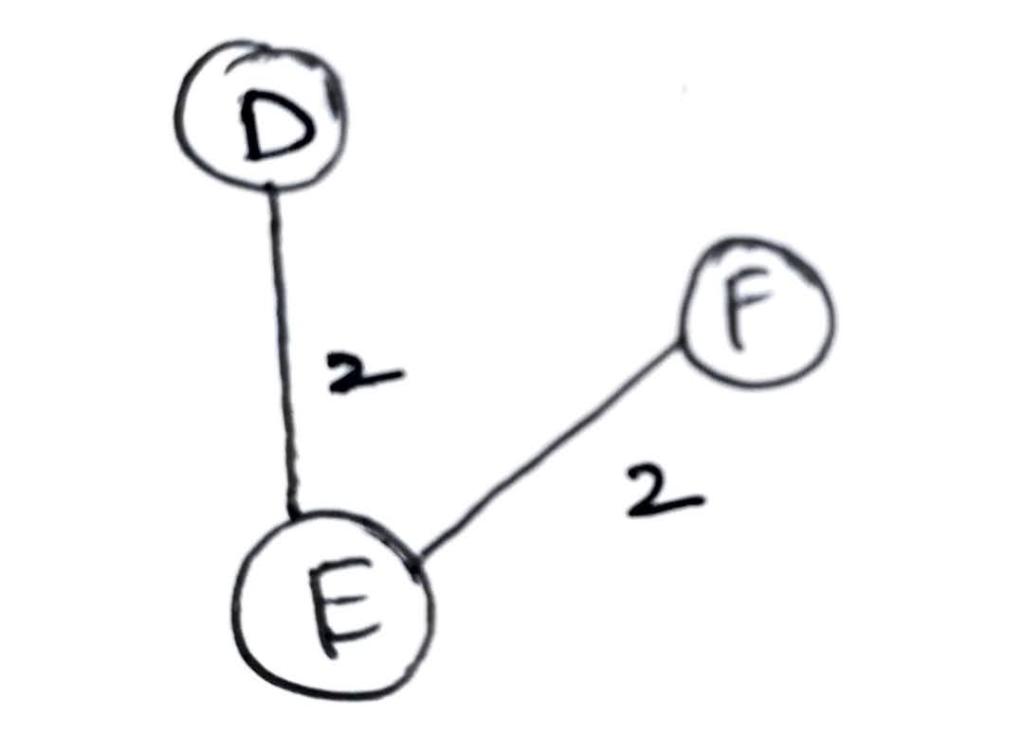
Step 3: From the root node E, select the path to which the edge weight is minimum out of the remaining connected nodes to the root. Here minimum weight is 2 compared to E->C which is 3. We are free to choose E->F or E->D. We choose here E->F.

Step 4: Considering F as a node, apply step 3. Now we have to consider the weights of the edges from the previous vertices i.e E in this case. Since E->D edge has minimum weight i.e 2 out of 3 (E->C) and 5 (F->D), we choose E->D.
Step 5: Repeat steps 3 and 4 until all the vertices are connected.
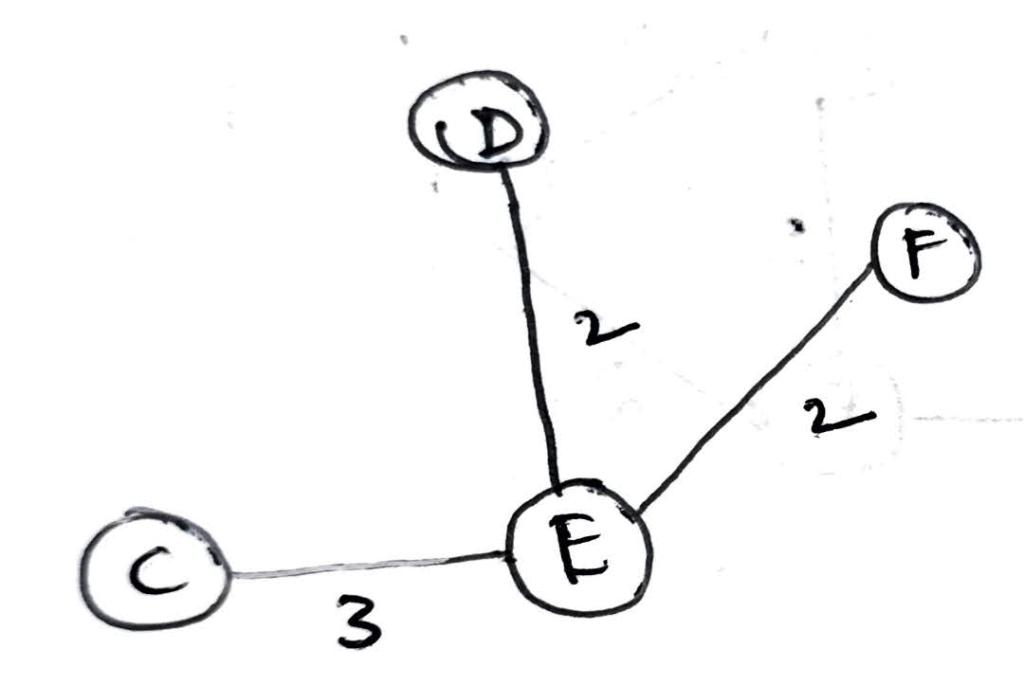
Fig. 1.5 
Fig. 1.6 
Fig. 1.7
Step 6: Exit.
In Fig. 1.7 we connected B->A as B-D forms a cycle, which is not acceptable.
Note 1: While choosing from E, we are free to choose any edge with weight 2 (in this case) i.e. E->F or E->D. If E->D is considered, at the later steps, we have to connect E->F.
Note 2: No.of Edges in Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)= |no.of vertices in given graph| -1
Note 3: The resulting MST should not form a cycle with any of the vertices.
Neologism:
Minimum Spanning Tree: A spanning tree of a graph is a collection of connected edges which include every vertex in the graph, but do not form a cycle. The Minimum Spanning Tree is the one whose cumulative edge weights have the smallest value.
7 thoughts on “Prim’s Algorithm”