We have seen Prim’s Algorithm for Minimum Spanning Tree. Dijkstra’s Algorithm, also known as Single source Shortest Path, is similar to it but we use it for graphs. When we are provided with a graph and a source vertex, this method is used to find the minimum distance of that particular vertex from the source vertex. This algorithm follows greedy method. It will be cleared once we go through an example.
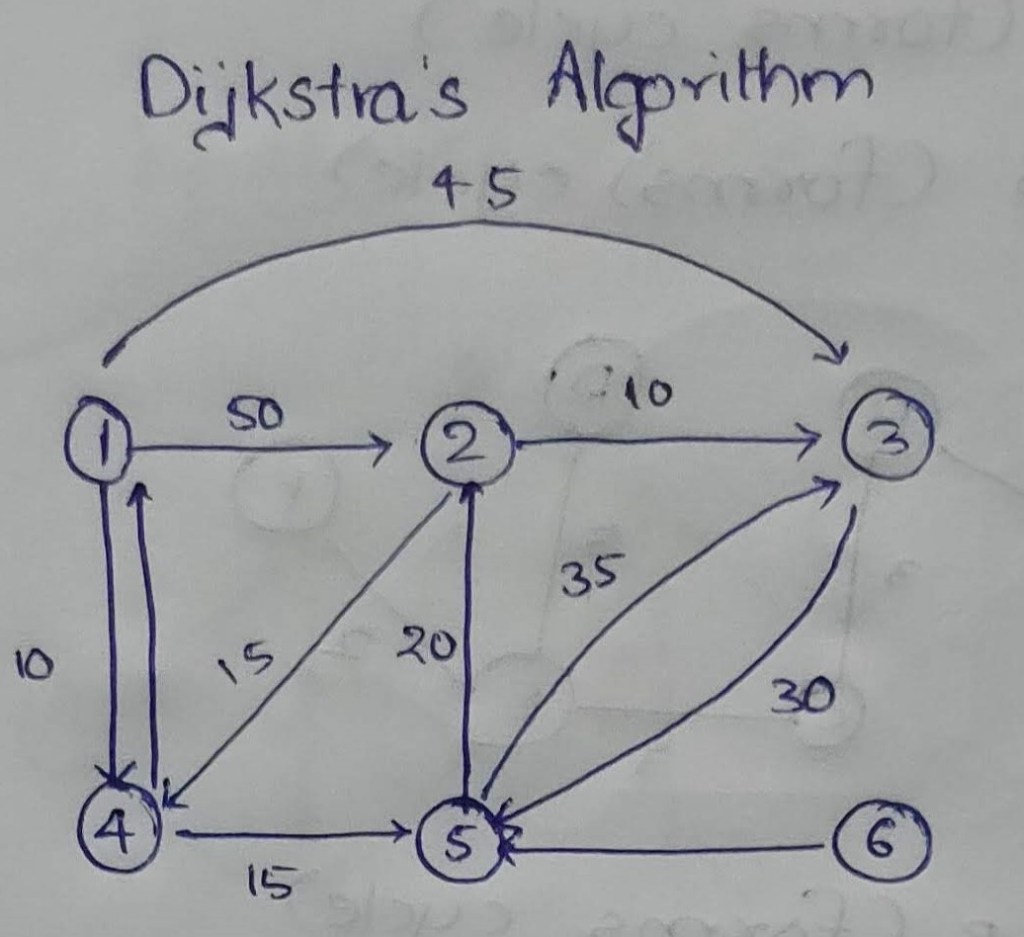
Let’s take the source vertex as ‘1’.
Algorithm:
- Create a table to keep track of the vertices selected and modified weights.
- From the source vertex (here 1), check the connected vertices (2, 3, 4).
- Mark those vertices with their distances from the source vertex (here 2 with 50, 3 with 45 and 4 with 10) and the other vertices as infinity (∞).
- Now select the next least weighted (or distance) vertex. Here 4.
- Now repeat the step 3. So, 5 will be marked as 25 as the distance from 1 to 5 via 4.. Earlier 5 was ∞ and now as the distance from vertex 4 is less than vertex 1 (∞), 5 was changed to 25.
- Since vertex 4 was already selected, we should go for the next least weighted vertex. Here 5.
- Continue step 3 till all the vertices are visited. This results us with the minimum distance from the source vertex.
- Stop.
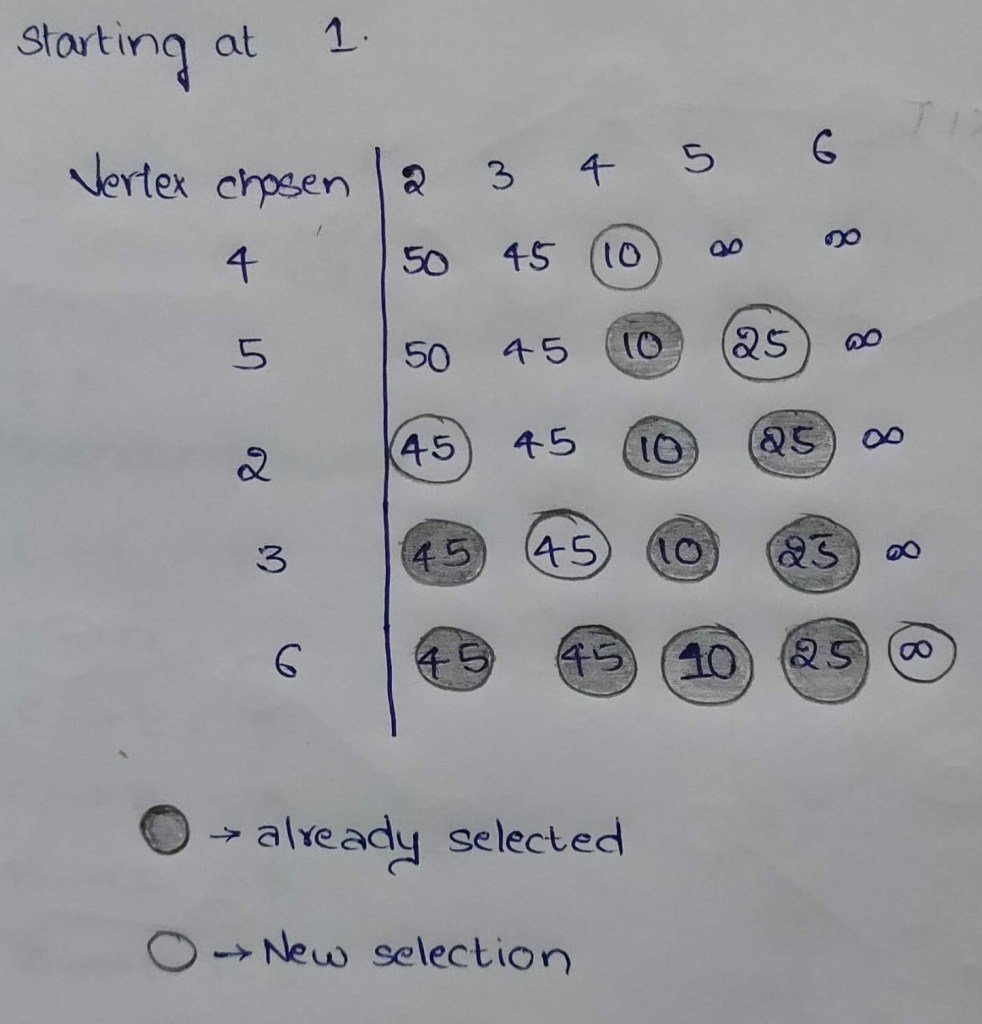
The selection is based on the distance from vertex 1. When the vertex chosen is 5 (in the table) then it was chosen along that particular column. For example, 50, 45, 10, 25 and ∞ are in the column 2. The vertex 5 is chosen as the distance from vertex 1 (root) is 25 i.e. less than all the distances.
Note:
- Once the vertex is selected then it should not be visited again.
- If there is no incoming edge to a vertex, it will remain ∞. In this case vertex 6.
- If two edges have the same distance or weight from the source vertex, any vertex can be selected. In this case, vertex 2 and 3 have same weight 45. So, we have selected 2 else 3 can also be selected.
Simple Math:
if (d[a] + w[a,b] < d[b]) then
d[b] = d[a] + w[a,b] //a,b are any vertices
Let's take a condition from our problem:
1(source) → 4(d=10) → (w=15) 5 (d=∞)
d=distance from source vertex
w=weight or cost of the edge
Here a is 4 and b is 5.
Applying the formula;
we have d[a]=distance of 4 from source vertex=10
d[b]=distance of 5 from source vertex=∞
w[a,b]= weight of the edge from 4 to 5 = 15
Now, d[a] + w[a,b] < d[b] => 10+15<∞ so, d[b]=25
This process of changing the distance of the vertex
from a source vertex is called Relaxation.
Relaxation can only be performed once on a vertex.
Disadvantage:
- This algorithm may or may not work for the graphs with negative weight edges.
Application:
- This can be used to represent business transactions in the form of graph.
- Shortest distance can be calculated to multiple places from a single point. Say from your home to holy places. Finding the best path so that we can cover all the places within less time.
- Used in Link state protocol which is one of the major routing algorithms.
4 thoughts on “Dijkstra’s Algorithm”