What is Merge Sort? Not remembering? We got you covered. Click here to revise Merge sort. Now, we shall look how we can improvise the conventional or traditional approach of Merge sort.
Note: This particular article has been derived from a research paper. The reference to the paper is provided at the “Reference and Recommendations” section. The pseudocode has been modified considering multiple constraints, so followed by code.
Algorithm:
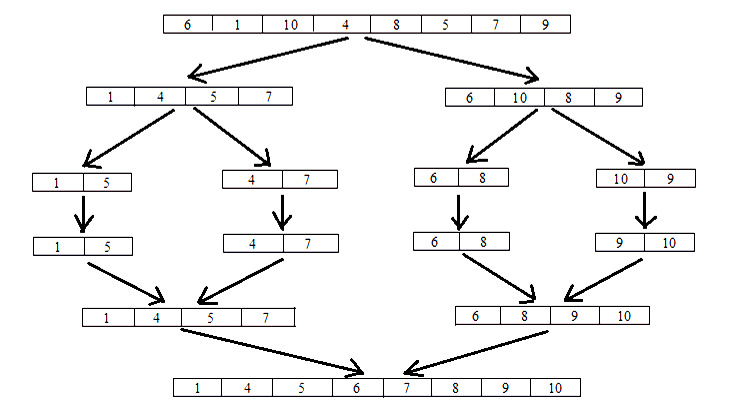
- Input the unsorted array
- Perform pair-wise sorting of each element of the array
- Divide the array into two sub-lists considering odd-even positions of the original array respectively
- Continue the above steps until the entire array is divided into sub-lists containing two elements each
- Merge and combine the sub-arrays
- Output the sorted array
Pseudocode:
START PROCEDURE
Merge (arr, l, mid, h )
s1 ← mid−l+1
s2 ← h-mid
Create arrays temp_left[s1] and R[s2]
FOR i ← 1 TO s1
DO temp_left[i] ← arr[l + i ]
END FOR
FOR j ← 1 TO s2
DO temp_right[j] ← arr[q + j+1 ]
END FOR
i ← 0
j ← 0
k ← l
WHILE i<s1 ^ j<s2 DO
IF temp_right[j ] ≤ temp_left[i]
THEN arr[k] ← temp_right[j]
j ← j + 1
ELSE arr[k] ← temp_left[j]
i ← i + 1
END IF
k ← k+1
END WHILE
WHILE i<s1 DO
arr[k]=temp_left[i]
i←i+1
k←k+1
END WHILE
WHILE j<s2 DO
arr[k]=temp_right[j]
j←j+1
k←k+1
END WHILE
END PROCEDURE
START PROCEDURE
func(arr,l,h)
m←0
k←l
WHILE k<h DO
IF arr[k]>arr[k+1] THEN
temp←arr[k]
arr[k]←arr[k+1]
arr[k+1]←temp
END IF
k←k+2
END WHILE
k←l+1
WHILE k<=h DO
a[m]←arr[k]
m←m+1
k←k+2
END WHILE
x←l
k←l
WHILE k<=h DO
arr[x]←arr[k]
x←x+1
k←k+2
END WHILE
k←0
WHILE k<m DO
arr[x]←a[k]
x←x+1
k←k+1
END WHILE
END PROCEDURE
START PROCEDURE
sort (arr,l,h)
IF l<h THEN
func(arr,l,h)
mid←(l+h)/2
sort(arr,l,mid)
sort(arr,mid+1,h)
merge(arr,l,mid,h)
END IF
END PROCEDURE
Notations
arr → Array
l → lower boundary of the array
h → higher boundary of the array
mid → Middle element of the array
sort() → Function to divide the sub arrays
based on odd-even positions
sort() → Function to sort the elements
merge() → Function to Merge the sorted elements
temp_left and temp_right → Temporary arrays for storing
the left and right sub-arrays.
Implementation of Enhanced_MergeSort in Java
import java.util.*;
class Enhanced_MergeSort{
static int n,i,j,k;
static void merge(int arr[], int l, int mid, int h){
int s1=mid-l+1;
int s2=h-mid;
int [] temp_left=new int[s1];
int [] temp_right=new int[s2];
for(i=0;i<s1;i++)
temp_left[i]=arr[l+i];
for(j=0;j<s2;j++)
temp_right[j]=arr[mid+1+j];
int i=0,j=0;
int k=l;
while(i<s1 && j<s2){
if(temp_right[j]<=temp_left[i]){
arr[k]=temp_right[j];
j++;
}
else{
arr[k]=temp_left[i];
i++;
}
k++;
}
while(i<s1){
arr[k]=temp_left[i];
i++;
k++;
}
while(j<s2){
arr[k]=temp_right[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
static void func(int arr[], int l, int h){
int a[]=new int[arr.length];
int temp;
int m=0;
int k=l;
while(k<h){
if(arr[k]>arr[k+1]){
temp=arr[k];
arr[k]=arr[k+1];
arr[k+1]=temp;
}
k=k+2;
}
k=l+1;
while(k<=h){
a[m]=arr[k];
m++;
k=k+2;
}
int x=l;
k=l;
while(k<=h){
arr[x]=arr[k];
x++;
k=k+2;
}
k=0;
while(k<m){
arr[x]=a[k];
x++;
k++;
}
}
static void sort(int arr[], int l, int h){
if (l < h) {
func(arr, l, h);
int mid = (l + h) / 2;
sort(arr, l, mid);
sort(arr, mid + 1, h);
merge(arr, l, mid, h);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int size=0;
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the size of the array: ");
size=s.nextInt();
int [] arr=new int[size];
System.out.println("Enter the elements of the array: ");
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
arr[i]=s.nextInt();
sort(arr, 0, arr.length-1);
System.out.println("\nArray after Sorting: ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; ++i)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
s.close();
}
}
Detailed explanation of code given in the downloadable file.
Time Complexity:
Both the conventional and proposed algorithms have a time complexity of O(n log n). But the basic difference between them is that the former method executes faster if the array size is quite large while the new algorithm sort the array by simultaneously dividing the array into odd-even position sub-lists. Before doing the division, it performs a pair-wise sorting of the array. As a result, the array becomes partially sorted. In this way, it takes less time to sort a small as well as a large list. Since Merge Sort has a wide application in various file storage and databases, a modified version of the technique puts fewer burdens to the programmer to have a quick access of an item. (Conclusion in the paper)
Thank you for visiting us. Kindly go through the below section For More!